The Internet in Japan
History
• 1984 Started in academia (UUCP-based)
• Keio University, Tokyo Institute of Technology, and Tokyo University
• 1988 Connected via Internet Protocol (IP)
• 1993 Commercial business started
• AT&T Jens and Internet Initiative (IIJ)
• In 2023
• A few hundreds of Internet Service Providers (ISPs)
• 4 mobile network operators (MNOs)
• 4 (commercial) internet exchanges (IXPs)
Top 8 Internet Service Providers (ISPs) on FTTH
| Company | Service name | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Softbank | Softbank Hikari |
| 2 | NTT resonant | OCN |
| 3 | NTT docomo | Docomo Hikari |
| 4 |
Sony Network | Communications So-net |
| 5 |
Biglobe | Biglobe |
| 6 |
Optage | eo Hikari |
| 7 |
KDDI | au Hikari |
| 8 |
Nifty | @Nifty |
Mobile Network Operators (MNOs)
| Rank | Company | Service Name |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | NTT Docomo | docomo |
| 2 | KDDI | au |
| 3 | Softbank | Softbank Mobile |
| 4 | Rakuten Mobile | Rakuten Mobile |
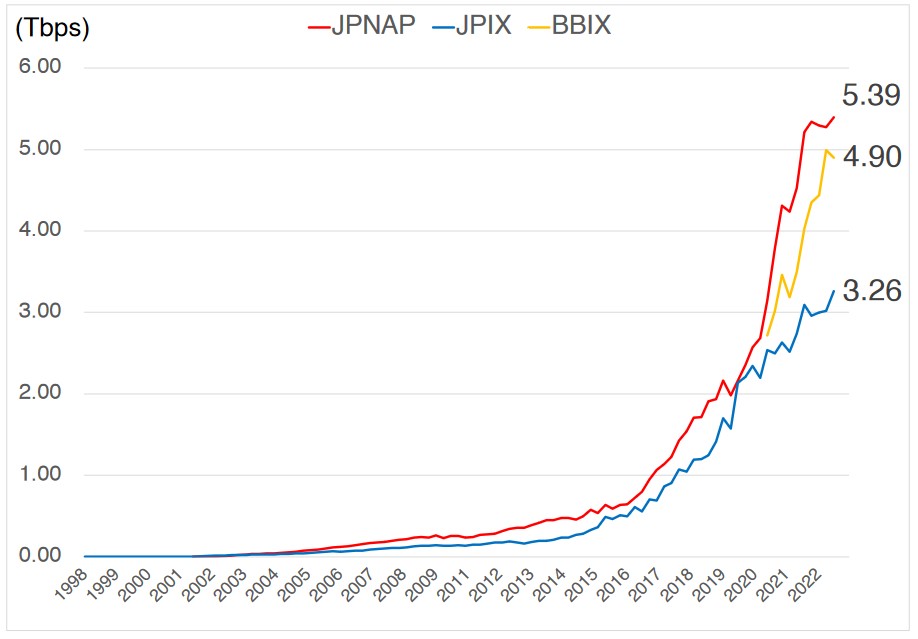
Internet Exchanges (IXPs)
| Rank | Company | Year to Start |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | JPIX | 1997 |
| 2 | JPNAP | 2001 |
| 3 | BBIX | 2002 |
| 4 | Equinix | 2007 |
Internet Penetration
• Internet usage rate (Individuals): 82.9%
• Nation-wide development rate of optical fibers: 99.3%
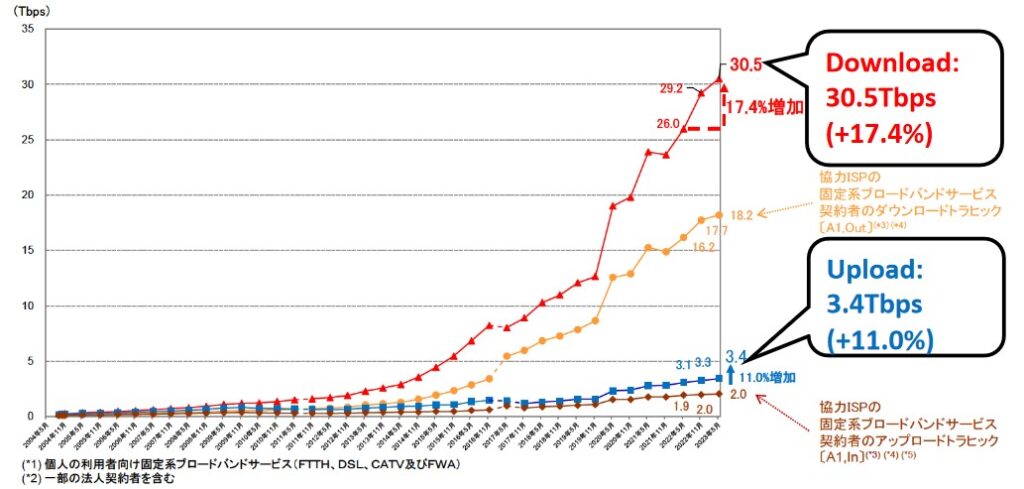
• Number of broadband subscribers: 43.8 million
• ISP (FTTH): 36.6 million
• CATV (HFC+FTTH): 6.5 million
• Mobile broadband subscribers (4G/5G): 184 million
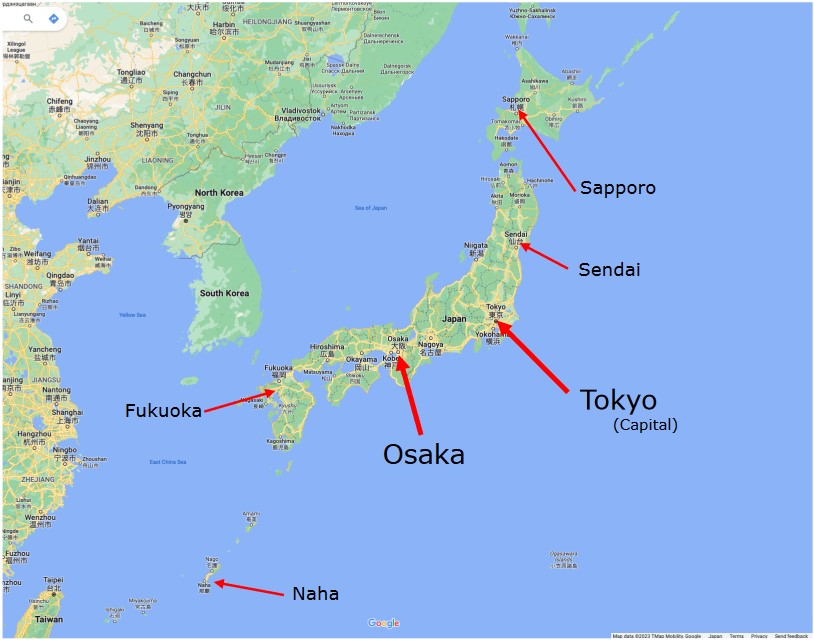
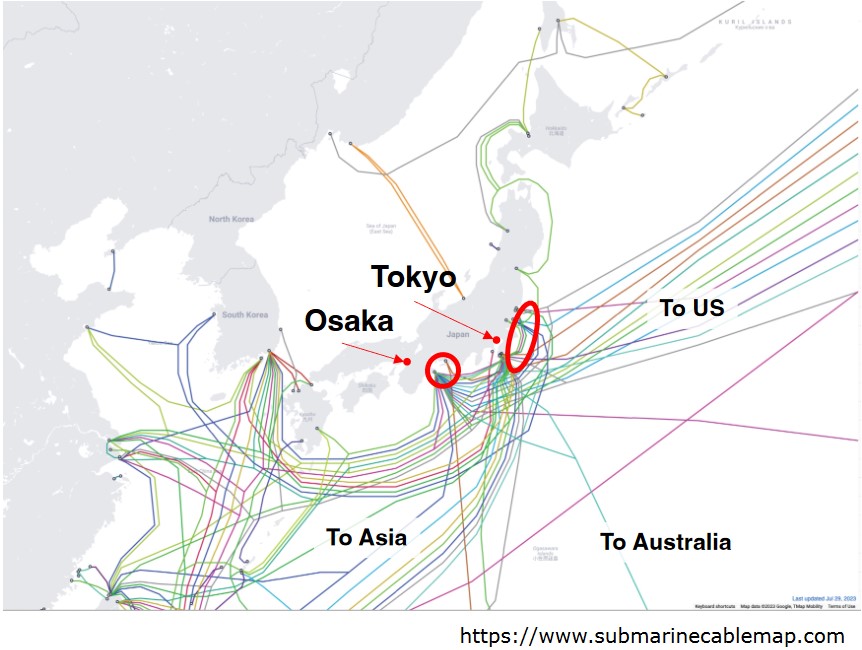
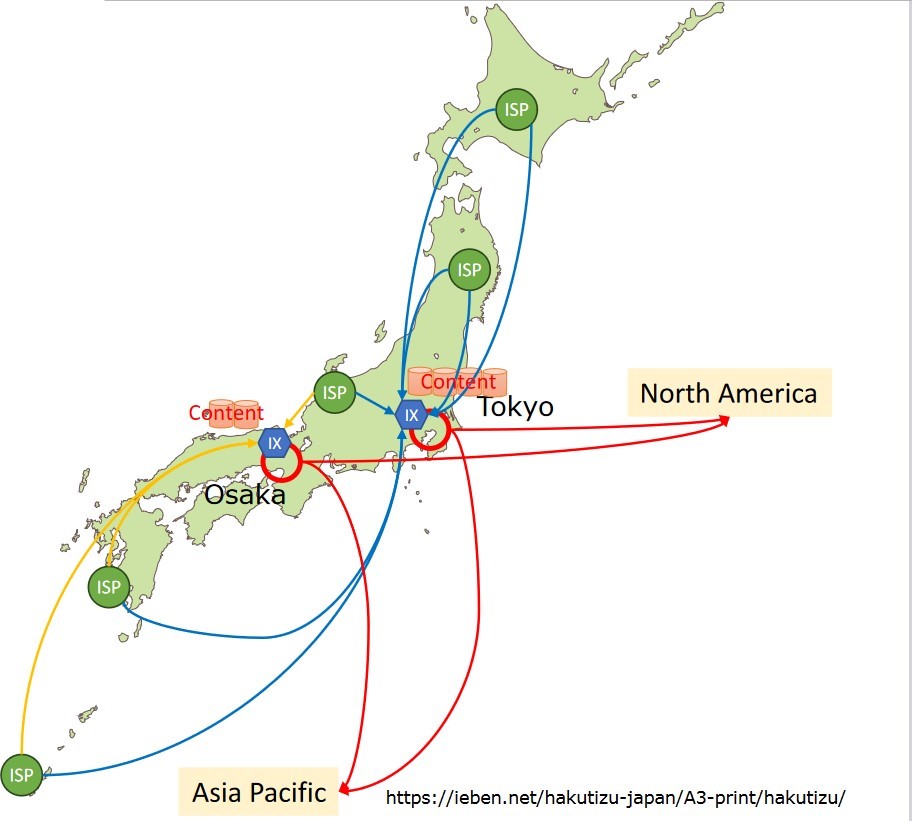
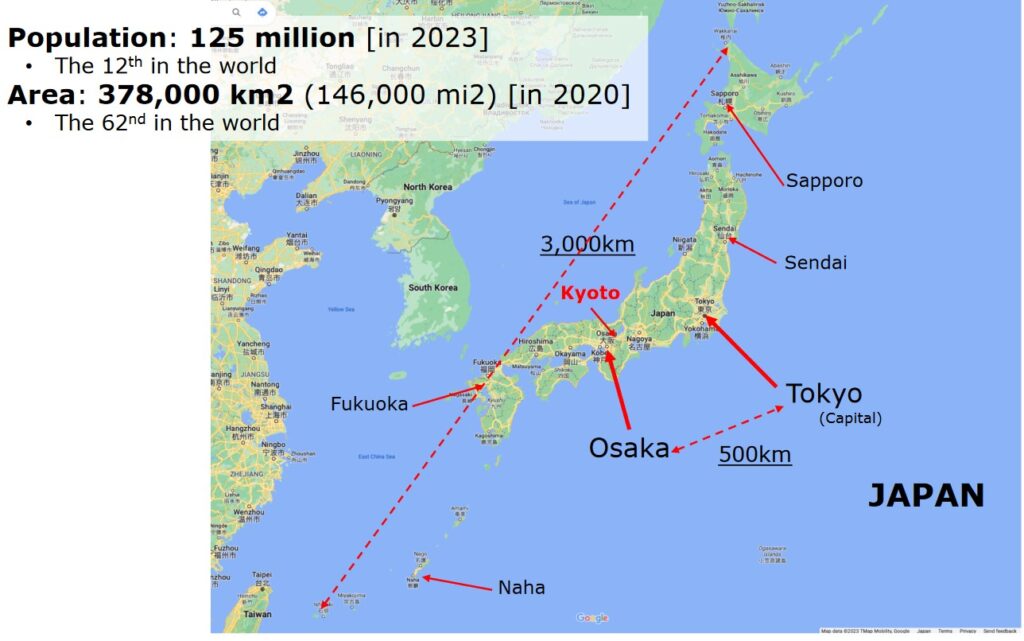
• Tokyo & Osaka
-Interconnection points
-Gateways to other regions
-Redundancy
Concern
• ISPs in east rely heavily on Tokyo, while
ISPs in west/middle connect to both
ASN ratio: domestic vs international
510 unique ASNs are connected to BBIX/Equinix-JP/JPIX/JPNAP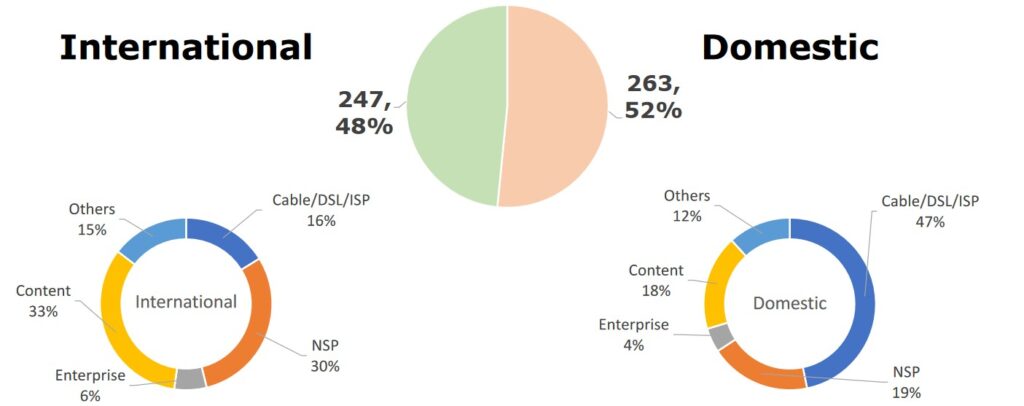
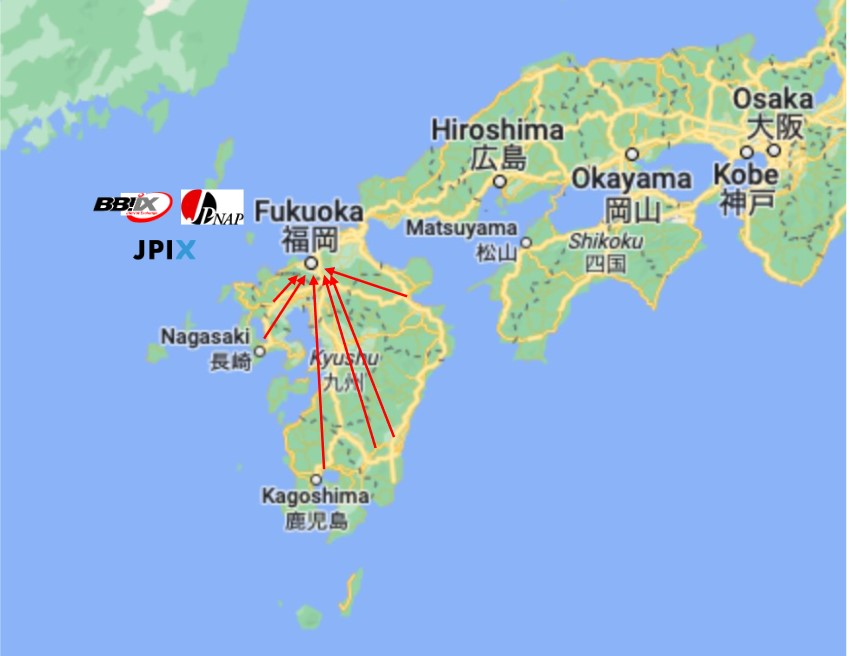
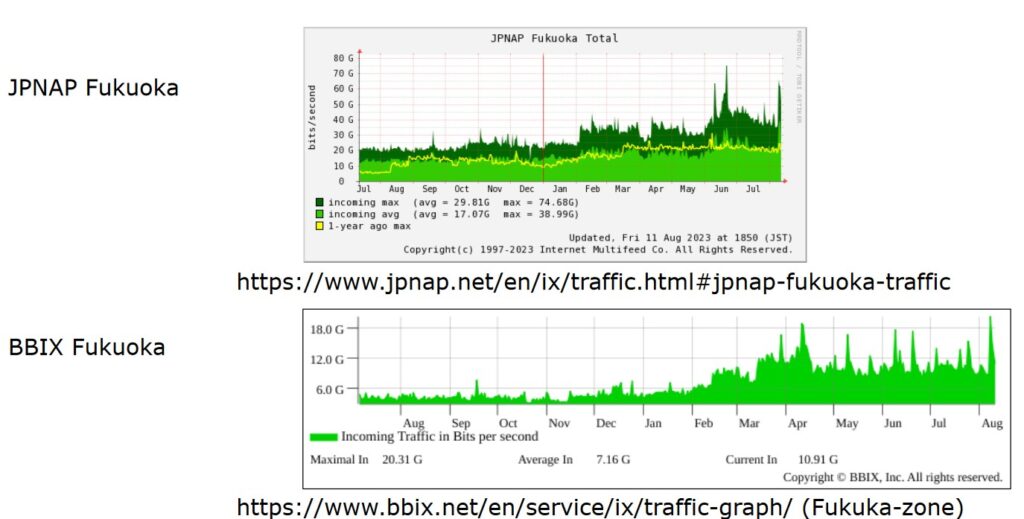
Fukuoka-third hub of Japan
Fukuoka
• A major city of Kyushu Island
• Three commercial Internet exchanges were built there
around 2021